Memory System Overview
Chorum’s memory system gives your AI persistent knowledge about your projects—patterns you use, decisions you’ve made, and rules that must never be broken.
Why This Matters
Most AI chat apps forget everything when you start a new session. You end up repeating yourself: “Remember, we use Zod for validation” or “Don’t use any types in TypeScript.”
Chorum remembers. When you switch projects or start a new conversation, your AI already knows the context.
Core Concepts
Project Memory
Each project in Chorum has its own isolated memory space. Patterns you establish in your “ChorumAI” project don’t leak into your “Marketing Site” project.
Learning Paths
Chorum extracts and stores four types of knowledge:
| Type | What It Captures | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Patterns | Coding conventions, recurring approaches | ”Use early returns to reduce nesting” |
| Decisions | Technical choices with rationale | ”Chose PostgreSQL over SQLite for multi-user support” |
| Invariants | Rules that must never be violated | ”All API routes require auth middleware” |
| Antipatterns | Things to avoid | ”Don’t use any type in TypeScript” |
→ See Learning Types for detailed explanations.
Embeddings
Under the hood, every learning is converted to a vector embedding—a numerical representation that captures its meaning. This enables semantic search: you can ask “What’s our error handling approach?” and find relevant patterns even if they don’t contain those exact words.
Memory Lifecycle
┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ LEARN │ ──► │ STORE │ ──► │ RETRIEVE │ ──► │ INJECT │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ Extract from │ │ Embed + │ │ Score by │ │ Add to │
│ conversation │ │ persist │ │ relevance │ │ LLM context │
└──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘- Learn — Chorum analyzes conversations to extract patterns, decisions, and invariants
- Store — Each learning is embedded and stored with metadata (type, timestamp, source)
- Retrieve — When you ask a question, relevant memories are scored and ranked
- Inject — Top-ranked memories are injected into the LLM’s context
Automatic vs. Manual Learning
Automatic Extraction
After each conversation turn, Chorum can analyze the exchange and extract learnings. The analyzer looks for:
- Explicit decisions: “Let’s use Zod instead of Yup”
- Established patterns: “We always validate input before processing”
- Stated constraints: “Never log PII to console”
Extracted learnings appear in your Pending Learnings queue for approval before being added to memory.
Manual Addition
You can also add learnings directly:
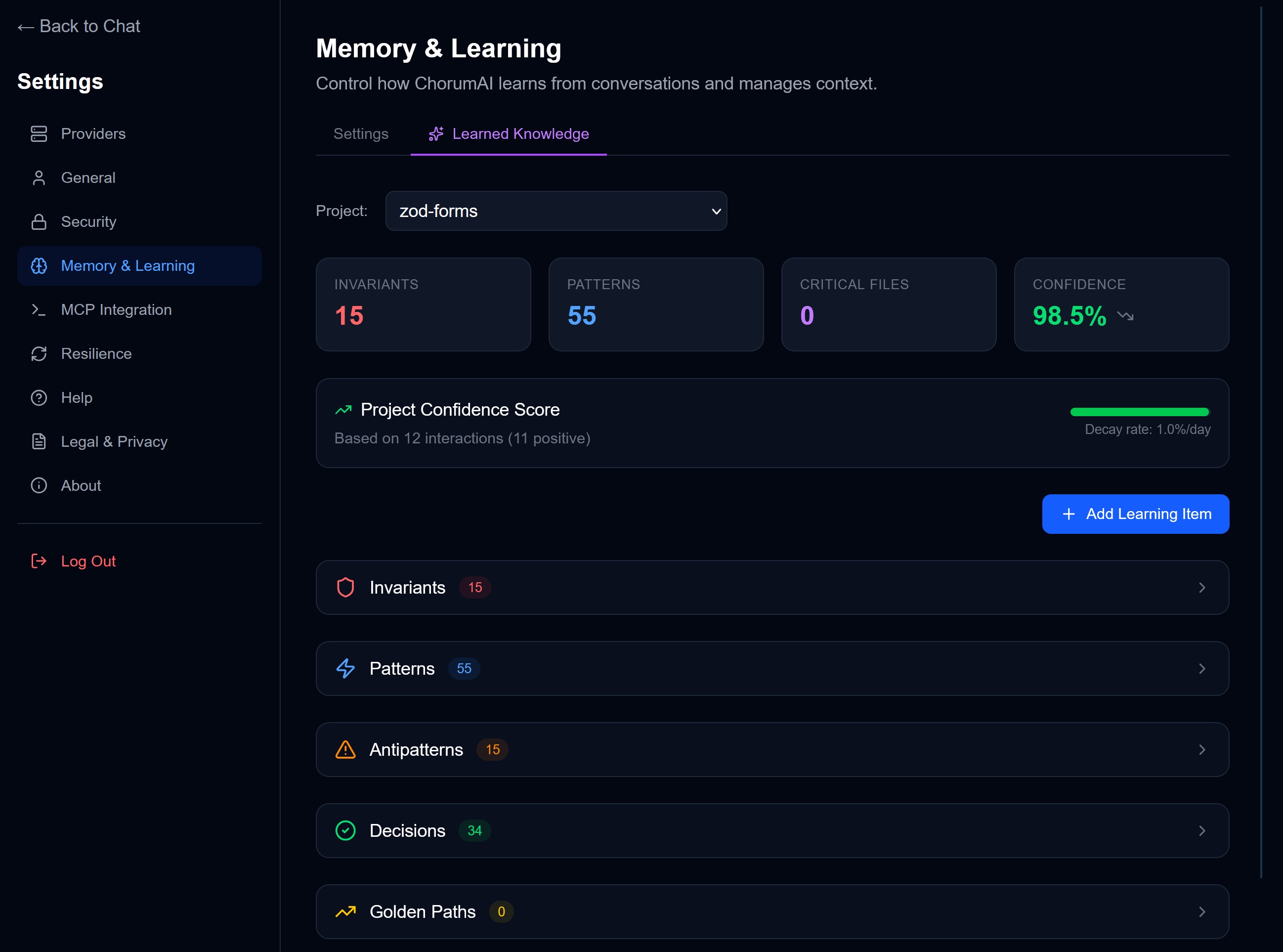
- Go to Settings → Memory & Learning → Learned Knowledge
- Click + Add Learning Item
- Choose type (Pattern, Decision, Invariant, or Antipattern)
- Enter the content
- Save
Manual learnings bypass the approval queue—they’re added immediately.
How Memory Affects Responses
When you send a message, Chorum:
- Classifies your query (trivial? complex? code-related?)
- Assigns a token budget based on complexity
- Scores all your learnings for relevance to this query
- Selects the highest-scoring items that fit the budget
- Injects them into the system prompt
The AI sees something like:
<chorum_context>
## Active Invariants
- Always use Zod for runtime validation
- Never store secrets in environment variables without encryption
## Relevant Patterns
- This project uses the repository pattern for data access
- Error handling follows the Result<T, E> pattern
## Recent Decisions
- Chose PostgreSQL over SQLite for multi-user support (Jan 20)
</chorum_context>This context grounds the AI in your project’s reality, reducing hallucinations and ensuring consistency.
Project Confidence
Each project has a confidence score (0-100) that reflects how well Chorum “knows” that project. Higher confidence means:
- More aggressive memory injection
- Lower relevance thresholds
- More trusted responses
Confidence increases with usage and diverse interactions. It decays slowly over time if you don’t use that project.
→ See Confidence Scoring for details.
Related Documentation
- Learning Types — Deep dive into patterns, decisions, invariants
- Relevance Gating — How Chorum decides what to inject
- Confidence Scoring — How project confidence works
- Memory Management — Viewing, editing, and deleting learnings
- MCP Integration — Exposing memory to external agents
“Memory isn’t just storage—it’s knowing what matters for this moment.”